In this brief analysis I look at whether plugin security updates are being applied to the most popular WordPress based sites.
Everyone knows WordPress is an incredibly popular platform for not only traditional blogs but also increasingly as a full blown content management system (CMS). This popularity combined with a wide attack surface makes it a popular target for malicious attackers. The wide attack suface is due to the thousands of plugins, themes and custom code.

Background on the Vulnerabilities
W3 Total Cache and WP Super Cache two of the WordPress communities most popular plugins were found to have a code execution vulnerability. An exploit that enables code execution is about as bad as it gets. New releases of the plugins were released on the 18th of April.
The following caching plugin versions are vulnerable
Version 1.2 and below of WP Super Cache
Six weeks after the release of the new plugins I dumped the HTTP Headers of the Internet's 100'000 most popular websites to get an understanding of how quickly web site administrators are applying critical web application patches.
A typical HTTP Header response from a site running WordPress and W3 Total Cache can be seen here. Notice the X-Powered-By Header, and the version of W3 Total Cache (0.9.2.4). Oops! We found a vulnerable site!
HTTP/1.1 200 OK Server: nginx Date: Mon, 06 May 2013 21:10:34 GMT Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8 Content-Length: 46122 Connection: keep-alive Vary: Accept-Encoding Last-Modified: Mon, 06 May 2013 20:45:07 GMT Accept-Ranges: bytes Cache-Control: max-age=604800 Expires: Mon, 06 May 2013 21:10:37 GMT X-Powered-By: W3 Total Cache/0.9.2.4 MS-Author-Via: DAV Vary: Accept-Encoding,Cookie
W3 Total Cache Version Analysis
W3 Total Cache was found to be running on 1310 sites out of 99590 that responded and 834 sites were found to be running WP Super Cache.
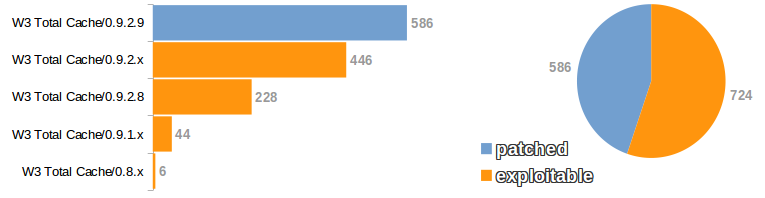
In a word its a massive FAIL. These web sites are the most highly trafficked in the world and only 44.7% have upgraded W3 Total Cache to the latest version. 724 websites are currently still vulnerable with code execution possible.
The WP Super Cache Header does not reveal the version number however it is likely that there is a similar percentage of vulnerable sites running that caching plugin.
Recommendations on Patching WordPress
Guides for securing WordPress are plentiful and patching is only part of that process. Keep in mind that managing a secure WordPress installation is an on-going process, the system needs to be maintained and updates applied as soon as possible after release.
Conclusion
One of the most surprising things about these results is the lack of security patch management in the top WordPress sites. It is to be expected that with literally millions of WordPress installations, finding vulnerable systems would be not hard, however the fact that there does not appear to be security patch management processes in place for even the high traffic sites is quite astonishing.
Next Level Your Technical Network Intelligence
- 13 Vulnerability Scanners
- 17 Free DNS & Network Tools
- 4+ Billion Records of DNS / IP data

Comments are closed.