Additionally, penetration testers or red teams needing to exploit Joomla targets will also find practical hints in this guide.

Read the new Joomla Security Testing Guide 2025 here.
Contents
Introduction to Joomla Security
Recent statistics show Joomla is a popular open-source Content Management System (CMS), with close to 6% of all websites.
It is open-source, free to download, and easy to use. These things make it a popular option. Similar to WordPress's plugins, Joomla allows functionality through "Extensions"
This popularity makes it a target for bad guys aiming to use a compromised web server for malicious purposes.
A lot of Joomla security holes arise from lack of maintenance, not taking passwords seriously, poorly coded extensions and even site backup's left in the web root.
Enumeration and Reconnaissance
Stage 1 is to discover as much technical information regarding the site configuration. This information is essential as it will aid us as we move onto the actual attacking or exploitation phase.
Now is the time to put yourself in the hacker's mindset. Enumeration or reconnaissance can be conducted stealthily with regular web requests used to gather technical information about the site. Or it can be conducted overtly by aggressively brute-forcing web paths to identify the presence of extensions.
- Joomla Identification & Version
- Joomla Extension and version Enumeration
- Modules
- Components
- Templates
- Plugins
- Languages
- Joomla Template Enumeration
- Enumerate Users
- Managers: content creation and backend system info.
- Administrators: admin functions except global options.
- Super Users/Administrator: ultimate power. Access all areas.
- Directory Indexing
- Network Service Discovery
- Bypass Sucuri or CloudFlare Web Firewall
- JoomlaVS & Other Tools
- Brute Force Joomla logins
- Exploit Joomla Extensions
To determine if the site is running Joomla, and identify the Joomla Core version, three simple methods can be used to determine the version of Joomla in use.
Meta Generator
Check the HTML source of the page for a meta generator tag in the HEAD section of the HTML source. This is the simplest way to determine if Joomla is being used.
This example is taken from the source of a default Joomla install.
<meta name="generator" content="Joomla! - Open Source Content Management" />
joomla.xml
To identify the version we can check the joomla.xml file within the directory /administrator/manifests/files/
https://www.joomla.org/administrator/manifests/files/joomla.xml
Result
/language/en-GB/en-GB.xml
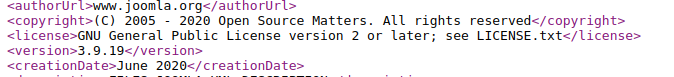
Another option to find the version is the language file.
https://example.site/language/en-GB/en-GB.xml <version> 3.6.5 </version>
Version in README.txt
If the meta tag has been disabled, check for the presence of /README.txt from the web root of the install. Joomla has the major version at the top of the ReadMe file.
Security Vulnerabilities in Joomla Core
Let's say a site with an older Joomla Core version is discovered by an attacker. This site may be directly exploitable via a security vulnerability in the Joomla core. It also shows the site is not being well maintained.
In a poorly maintained site, other components, such as Extensions or Templates, may not be updated. The likelihood of a successful attack has dramatically improved.
Similar to WordPress's plugins, Joomla allows functionality through "Extensions"
Extensions are broken down into a few types:
All can be installed as required. Vulnerabilities can arise in any of these when poorly coded, an example could be non-logged in users having access to the same features as logged in users.
Enumeration is attempting to find as many installed extensions as we can, including disabled extensions. Knowing these extensions may allow us to identify the version, and research whether it is vulnerable to known exploits.
Unfortunately, unless you have the administrator account details, there is no easy way to find every single extension of a particular Joomla install.
It is worth noting Joomla has a live list called - Vulnerable Extensions List (VEL)
This list is of vulnerable extensions for which no patch is known to exist. It can be used as a source of information or a place to start when looking at a Joomla site.
Passive
Hints to the extensions and modules present in a site may be found in the HTML source of the page. Once, an add-on is identified additional information can be gathered from the manifest file.
Active
Some extensions do not leave traces in the HTML source. To find all the installed extensions you have to be more aggressive. Several tools can brute force known extension/component list. There is no one size fits all when it comes to Joomla. Using a combination of available tools will get the best results.
One example is the Metasploit Joomla Plugin Scanner. This metasploit auxiliary module uses a wordlist to locate valid paths scanning for extensions and vulnerabilities.
Extension Version Enumeration
You have compiled a list of extensions of the site, now for the version. The design of Joomla means this information isn't forthcoming or comprehensive, especially when attempting to find it quietly.
It is possible you may find the extension version in a manifest file or other resources such as the addon's stylesheets or javascript.
With a valid version you can compare what has been found against known exploits. This comparison will attest if the site is likely vulnerable, before throwing any exploits.
As with extensions, Joomla Templates can contain vulnerabilities that may expose the site to compromise. Templates are simply collections of PHP code with HTML and CSS resources. Complex templates have additional components and are more prone to security vulnerabilities.
Enumeration of the template is conducted similarly to detecting the extensions. Inspect the HTML and locate the template. Alternatively, run a passive scan on Hacker Target's Joomla Security Scan and scroll through results to find the Joomla Template.

One important factor when testing for vulnerable Joomla Templates and components is where it may be installed but not active; as the code is still accessible it may still be vulnerable. For this reason, brute force testing for template paths is an additional step when assessing an unknown Joomla installation.
A quick tip is first see if the Administrator login page is publicly available.
https://exampledomain.com/administrator
There is no simple way to do this manually in Joomla as opposed to WordPress where it may be possible to iterate through the users using a simple bash one-liner.

With Joomla, it requires guesswork. All new installs have a 'Super Administrator account' called admin. As part of the install, Joomla requests a password for this account. Joomla also suggests changing the name of the account from 'admin' to something more difficult to guess.
This makes it complicated for a dictionary-based attack against the admin panel.
Enumerating users through Guessing
Start with the common one admin and go from there.
Joomla doesn't seem to allow direct listing all users and / or leak their information.
A default install of Joomla allows 3 privileged user groups which have access to the control panel:
Note: from version 3.2 two-factor authentication was implemented as a core feature. Admins can enable it from User Manager in the Control Panel.
Password Re-use and Breach Datasets
A common technique used in targeted attacks is mining breach datasets for passwords. If a user is breached on another site, there is a chance they will use the same password or a variation on the password on other sites. Working from a targeted domain passwords can quickly be found especially in larger organisations.
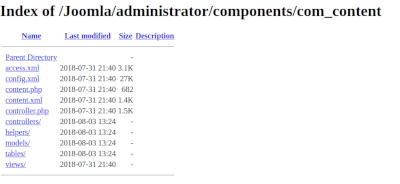
A misconfigured server can allow you to view the contents of a directory in a web-accessible path.
Viewing the contents of the directory allows an attacker to gather sensitive information not intended for public viewing about the existence and contents of the files. Such as hidden files, backup files, config files, plugins, and templates, without the need to brute force the paths.
Start by browsing to folder locations and see if you get a 200 OK HTTP response and see a list of files / folders in the browser.
Here we are checking network services. The main technique used for identifying the servers attack surface is Port Scanning.
An Nmap port scan will identify the network services listening on the server. These could include FTP, SSH, Webmin or even the web server itself. Working from the results of the Port Scan an attacker would identify server applications, versions and look for exploitation opportunities.
If the Joomla site is protected by Sucuri or CloudFlare, exploits that might otherwise succeeed could be blocked. Even various reconnaissance techniques can be blocked by these web based firewall (WAF).
By knowing the real IP address of the server it is likely we could bypass the server simply by putting an entry in the clients /etc/hosts file. This works because we bypass the sites DNS that would otherwise send us via the Web Firewall.
Historical DNS Records
A common method is using historical DNS records to identify the real IP address.
Historical DNS records may show the original IP address before the firewall service was implemented.
Mail Records (MX), if mail is hosted on the same server as the website then this will reveal the real host
TXT SPF, records might also reveal IP addresses of interest
TLS / SSL Certificate Searches
TLS / SSL searches against Certificate Transparency Datasets may also find real hostnames associated with the sites actual IP address if they can matched.
Passive Joomla Security Scan
Hacker Target hosts a free and simple to use passive Joomla scan. Discover vulnerabilities, web server details, configuration errors, identify template, and test for directory indexing and others.
The freely available tools perform analysis from a simple page grab. Through the examination of the HTML source code, javascript, and a few other open publicly accessible pages, it is possible to gain immediate insights into the state of security on the target site. This is applying only passive analysis methods, without sending any aggressive security scanning.
JoomScan
JoomScan is the OWASP Joomla! Vulnerability Scanner. An open source project written in Perl. Ties some of these enumeration techniques together such as the Joomla version, vulnerabilities and the admin login page.
Check out the the latest version from github https://github.com/rezasp/joomscan
Note this project has not been updated for a number of years
JoomlaVS
JoomlaVS is an Open source Ruby application. Scan for vulnerabilities in components, modules and templates and basic fingerprinting. More info available on the projects at https://github.com/rastating/joomlavs
----------------------------------------------------------------------
??? ??????? ??????? ???? ??????? ?????? ??? ???????????
?????????????????????????? ???????? ??????????? ???????????
?????? ?????? ????????????????? ??????????? ???????????
?? ?????? ?????? ????????????????? ???????????? ????????????
????????????????????????????? ??? ?????????????? ??? ??????? ????????
?????? ??????? ??????? ??? ?????????????? ??? ????? ????????
----------------------------------------------------------------------
[+] URL: http://testexample.com/
[+] Started: Mon Jun 12 11:02:01 2020
[+] Found 1 interesting headers.
| Server: Apache
[+] Joomla version 2.5.30 identified from language file (en-GB.xml)
[!] Found 8 vulnerabilities affecting this version of Joomla!
[!] Title: Joomla Akeeba Kickstart Unserialize Remote Code Execution
| Reference: https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/35033
| Reference: http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2014-7228
[i] Fixed in: 3.3.5
[!] Title: Joomla Media Manager File Upload Vulnerability
| Reference: https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/27610
| Reference: http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2013-5576
[i] Fixed in: 3.1.5
[!] Title: Joomla 2.5.x Language Switcher ModuleMultiple Cross Site Scripting Vulnerabilities
| Reference: https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/37473
[i] Fixed in: 3
[!] Title: Joomla 1.5 - 3.4.5 - Object Injection Remote Command Execution
| Reference: https://www.exploit-db.com/exploits/38977
| Reference: http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2015-8562
[i] Fixed in: 3.4.6
[!] Title: Remote Code Execution in third-party PHPMailer library
| Reference: http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2016-10033
| Reference: http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2016-10045
[i] Fixed in: 3.6.5
[!] Title: Unauthorised Logins
| Reference: http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2014-6632
[i] Fixed in: 3.3.3
[!] Title: Denial of Service
| Reference: http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2014-7229
[i] Fixed in: 3.3.4
[!] Title: Joomla! < 3.6.4 Privilege Escalation
| Reference: http://www.cvedetails.com/cve/CVE-2016-9838
[i] Fixed in: 3.6.4
[+] Scanning for vulnerable components...
[!] Found 0 vulnerable components.
------------------------------------------------------------------
[+] Scanning for vulnerable modules...
[!] Found 0 vulnerable modules.
------------------------------------------------------------------
[+] Scanning for vulnerable templates...
[!] Found 0 vulnerable templates.
------------------------------------------------------------------
[+] Finished
CMSMap
As the name implies, CMSMap covers the most popular of the CMS's. An open source project written in Python, this tool has support for Joomla, WordPress and Drupal. Useful for automating a scan for low-hanging fruit.
Download the latest version of CMSMap github: git clone https://github.com/Dionach/CMSmap
Attacking and Exploitation
2013 Joomla 3.2 stable release bought 2FA as part of the core install which adds another challenge to brute-forcing an account. But it isn't enabled by default.
Popping Weak Passwords
Detecting weak passwords for Joomla comes in a variety of ways. There are many ways to to brute force a login page, here are a few.
Nmap NSE Scripts for Joomla
NMAP is most known for network discovery, however, NSE scripts extend the functionality of the popular NMAP port scanner. An Nmap NSE script is particularly helpful for performing a brute-force password play against a Joomla install.
$ nmap -p80 http-joomla-brute example-site
Burpsuite
If there is a login form on the site or you have found the administrator interface, then burp suite can be used to try to brute force the password.
There are other tools around such as JoomBrute, and others such as Hydra and Ncrack, though the latter two are most suited for other protocols.
Metasploit
Rapid7's Metasploit provides a few modules for brute forcing CMS and Joomla for various Joomla versions. One is the Joomla Bruteforce login utility
msf > use auxiliary/scanner/http/joomla_bruteforce_login
Keeping the Joomla extensions, core and templates updated and/or patched needs to be a routine task for the Joomla administrator of the site.
