Poor security patching is a problem across all aspects of information technology. WordPress administrators are not the only ones struggling to keep things patched; in May 2019, the Baltimore city council servers were taken out in a ransomware attack. Even the phone in your pocket needs to be patched, with reports estimating that over a billion Android phones are missing security patches.
Automattic and WordPress have worked hard to make keeping things updated a smooth and easy process. When your software runs on 30% of the world's websites, patch management is important.
Keep in mind that for many WordPress sites, there is no full-time IT administrator. Almost anyone can get a WordPress site running. It's the ongoing patching and management many struggle with, which has led to growth in Managed WordPress hosting and services.
CMS Detection Methodology
The methodology used to determine the underlying technology of web sites is to search for specific strings within the HTML, or the HTTP Headers provided by the web server. For WordPress, our process is a simple matter of downloading the headers and page source from all sites in the Alexa top 1 million sites. The resulting content was then searched for /wp-json/, /wp-includes/ or /wp-content/ indicating a WordPress powered site.
No guarantee is made to the accuracy of this data. The accuracy comes down to what we found in the source.

CMS Usage in the Top 1 Million Sites
Comparing WordPress against its rival content management systems. It is clear to see WordPress is well out in front in 2019.
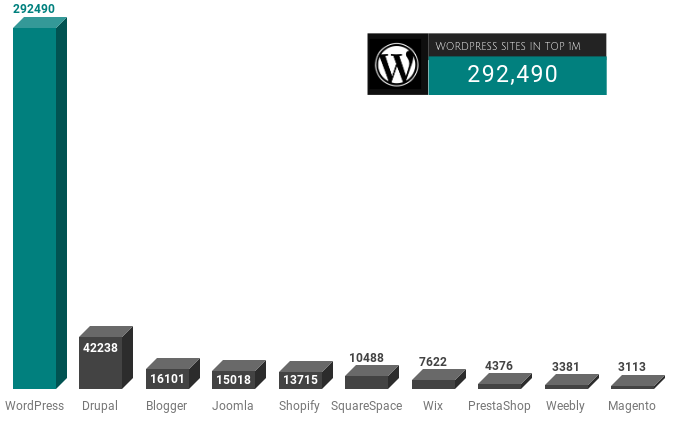
The popularity of WordPress gets quoted in everything from marketing materials to security incident reports. It is nice to see that the often quoted 30% figure is close even when counting the worlds highest traffic sites.
Web Servers of the Top 100K WordPress Sites
These statistics are based on the front-end web server delivering the WordPress site to the browser. The results are based on the initial HTTP header (Server:).
In the following chart, the total number for the web server technology is the focus.
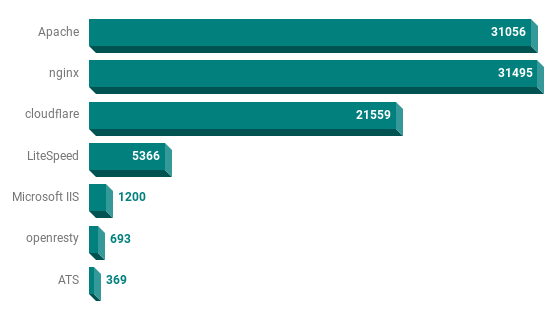
Keep in mind the front-end servers powering Cloudflare are Nginx based, and the growing openresty is also built on Nginx. Putting Nginx well out in front as the technology of choice serving the page to the browser. No doubt one of the reasons it was recently acquired by F5 Networks.
 More than a handful of sites are running on Microsoft based IIS servers (1275). Included in this number are WordPress powered Microsoft Corporation properties such as Visual Studio.
More than a handful of sites are running on Microsoft based IIS servers (1275). Included in this number are WordPress powered Microsoft Corporation properties such as Visual Studio.
A closer look at the Cloudflare statistics
In this breakdown of the WordPress sites being served by Cloudflare sites, we can see Cloudflare has grown by a couple of percent since our last analysis performed in 2017.

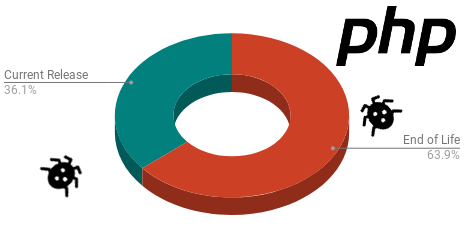
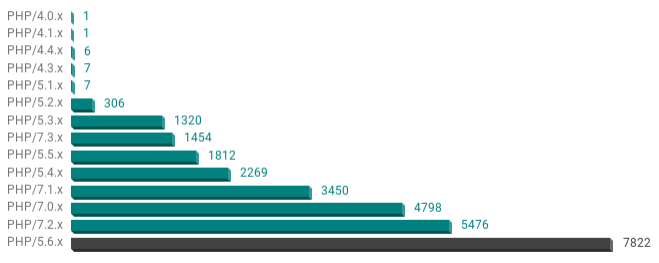
Don't forget your PHP Upgrades
In the HTTP Header responses, we found the PHP version leaking in 28729 sites (28.7%) of the top 100'000. This was found in the X-Powered-By header or in the extended Apache Server Header. The end of life chart shows the percentage of sites within the 28.7% where the version was leaked.
Keep in mind that anything before PHP/7.1 is End of Life and not supported at all from the PHP project - even for critical security patches.
Analysis of installed WordPress Core Version
WordPress Security recommends always run the latest version of WordPress core to ensure security fixes are applied.
There are different ways to determine the version test of a WordPress installation. For simplicity, only sites with the default Meta Generator banner are included in this break down of versions found. The default generator tag was found on 60009 of the top 100K WordPress sites.
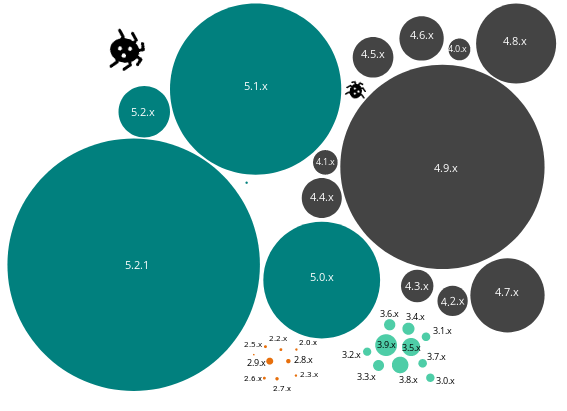
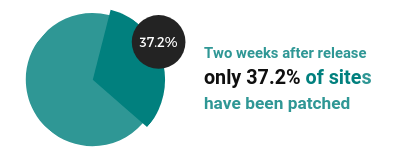
Just over a third of all the sites are running the latest version 5.2.1 (this was the latest version at time of analysis - 3rd June 2019). Version 5.2.1 had been out for 2 weeks at this time.
Only 37.2% of these high traffic sites are running the latest version (2 weeks after release).
All this indicates a lack of standard maintenance procedures on the majority of sites. Administrators still need to improve the adoption of best practice security maintenance processes.
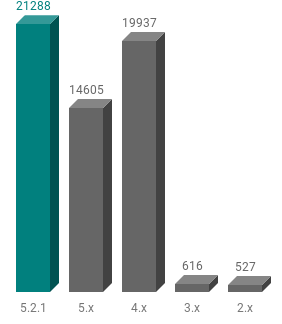
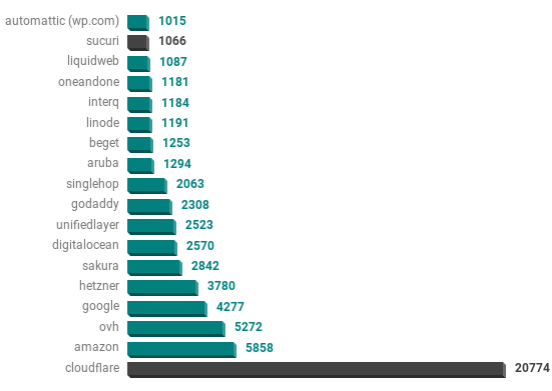
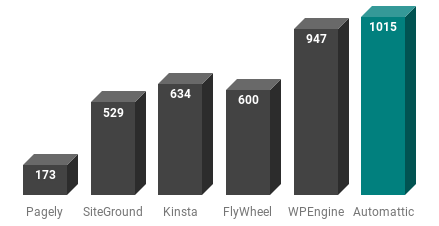
WordPress Hosting Providers
Crunching the numbers for the hosting of the WordPress sites, we simply resolved the IP address of the site. From the IP address, the network block owner was determined by running a simple ASN lookup.
The results show the owner of the hosting net block which is often the hosting provider. Note: some hosting companies may not own the IP block. In these cases, large networks such as Amazon (AWS) and Google (GCP) will include smaller hosting companies.
Managed WordPress Hosting
For example, the statistics for the Google ASN include the managed hosting provider Kinsta who utilizes Google Cloud for their services.
The data for these managed hosting providers has been pulled from HTTP headers, where clues exist in the server header or other custom headers.
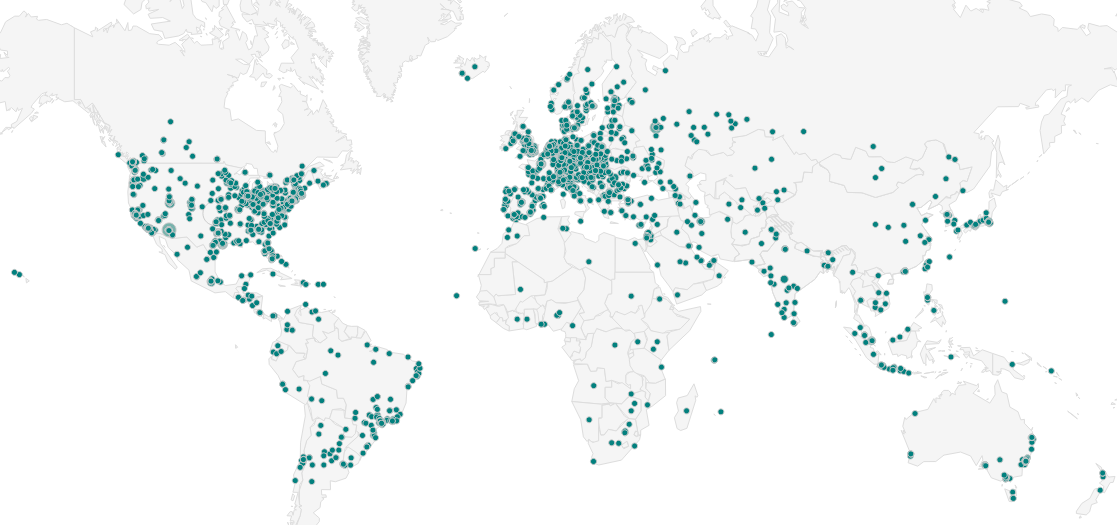
Hosting Locations
Everyone loves a good map. Utilizing the Maxmind GeoLite data the IP address locations were plotted against the list of 100'000 top WordPress sites.
As you can see, either a few sites are running on submarines in the Indian Ocean or, the IP Geolocation data is not 100% accurate. The general distribution of sites around the world is interesting, with expected clusters in the data centres within the USA and Europe.
Network Services
Interesting to see that nearly 10% of the top sites are running SSH on port 2222 or 22222.
It seems server owners do not like SSH password bots smashing away all day and night and filling their log files.
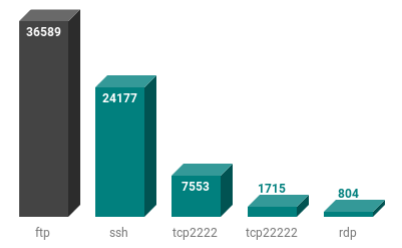
Are 36% of the top 100000 WordPress sites updating files using the unencrypted FTP protocol? Let's hope not. It is, of course, possible to use FTP over TLS/SSL, and this can be configured to work over port 21. Let's hope all those high value sites are using encrypted communication.
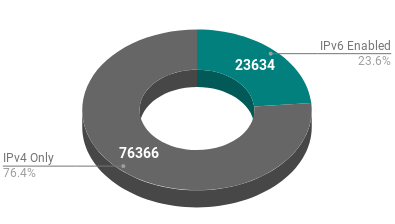
IPv6 Adoption in the Top WordPress Sites
Google has statistics indicating they are seeing 29% of traffic being IPv6 globally. Maybe its time that web site owners jumped on the IPv6 wagon.
WordPress Plugin and Theme Analysis
Analysis of WordPress plugins is limited to those that are detectable through passive analysis. In this instance, passive analysis is through examination of a regular web request and parsing the HTML and HTTP headers. More aggressive plugin detection can be achieved through brute-forcing plugin paths. Check out our guide on Attacking WordPress Sites However, this generates thousands of web requests and is only used by malicious actors and vulnerability scanning tools.
SEO Plugins
- WordPress SEO by Yoast
- All in One SEO.
The nice thing about these plugins is they put a comment in the HTML source, allowing it to be identified. Recently, a new contender has entered the scene - SEO Framework. According to the stats, it has plenty of ground to cover to catch up.
Compared to 2017, Yoast SEO has really hit the accelerator now with 82% of the install base (of sites running an SEO plugin).
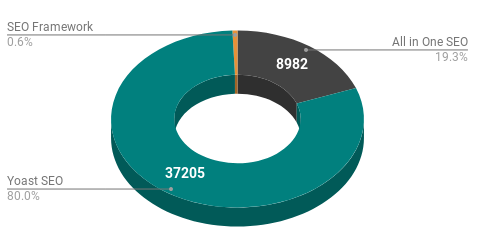
We can see that of the 37205 sites running Yoast, 5958 of these are running the Yoast Premium Plugin. That's 6% of the top 100K WordPress sites on Yoast Premium. Well done guys. 🙂
Identification was performed by checking for the plugins default comment. Of course it is possible that some sites have removed the comment.
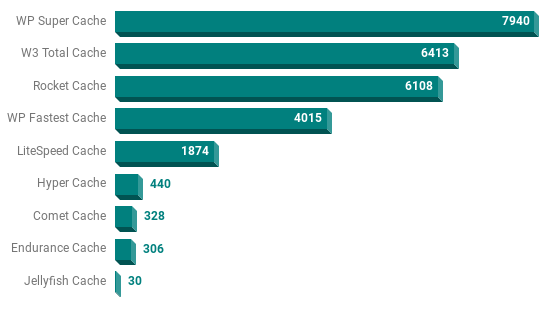
WordPress Caching Plugin Showdown
Fast sites make users happy. They also make Google happy following the update to the search algorithm that takes site speed into account. Understandably these factors make WordPress Caching Plugins a popular choice for most serious sites.
The most popular caching plugins include comments in the HTML (by default) identifying the plugin in use. By searching for these comments, it was possible to gather numbers for the most popular caching plugins.
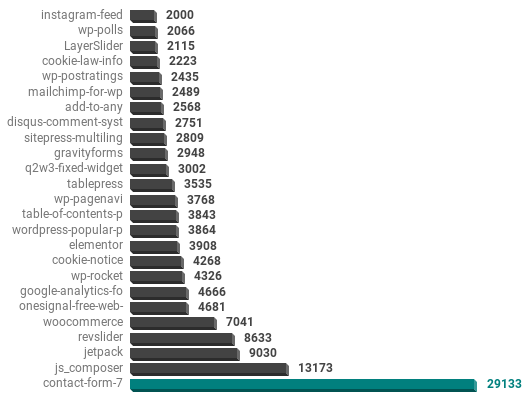
Top 25 WordPress Plugins
The numbers become a bit rougher when determining the plugins in use. Unless the plugin has a default comment in the code, such as the SEO plugins and caching plugins, it gets a bit harder to determine plugins in use.
Many plugins load resources from the plugin folder (css or js), and this is the best way to identify plugins used passively.
So to determine the Top 25 plugins listed below, the HTML was searched for /wp-content/plugins/$plugin/. Then the plugin names were extracted simply using the path. An additional caveat: it is now common for javascript and css to be minified to improve site performance. If minified code is in use, this method of identifying plugins no longer works.
Top 25 WordPress Themes
Using a similar methodology as the above plugin identification, we were able to identify the WordPress theme in use. Searching for the path /wp-content/themes/$theme/ in HTML and counting the most common occurrences. Many sites will use custom themes and have changed the path, however, identification of the most common should be fairly accurate using the large sample size.
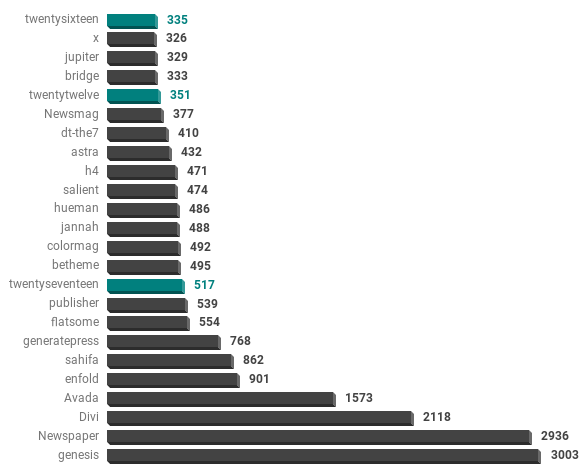
It is interesting to note that even the default themes (twentysixteen, twentyseventeen) that ship with WordPress make an appearance in the list. Showing that a flashy theme does not make the site, content matters.
Download full list of 100K WordPress Sites in .csv
Format of the
csv file is comma separated with columns $rank,$alexarank,$site.Article updated June 2019.
