Firewall Testing is the most reliable way to confirm whether a firewall is working as expected. Complicated firewall rules and poor management interfaces can make it difficult to determine the status of a firewall or Internet facing router. By using a remote port scanner it is possible to accurately determine the firewall status from an extenal perspective.
This type of firewall test attempts to make connections to common external facing services from the same perspective as an attacker. In other words it attempts to make connections from outside your local network. Open services can be identified and closed or blocked depending on your requirements.
Quick Online Firewall Test to identify open ports on an Internet facing system. Accuracy is assured by using the world famous Nmap port scanner.
Ports Checked in Free Scan:
21 File Transfer (FTP)
22 Secure Shell (SSH)
23 Telnet
25 Mail (SMTP)
80 Web (HTTP)
110 Mail (POP3)
143 Mail (IMAP)
443 SSL/TLS (HTTPS)
445 Microsoft (SMB)
3389 Remote (RDP)
With a valid membership play at the next level on our full featured Online Nmap Port Scanner.
Valid Input: IPv4 IPv6 scanme.nmap.org 8.8.8.8 2001:4860:4860::8888
Why You Need an External Firewall Test
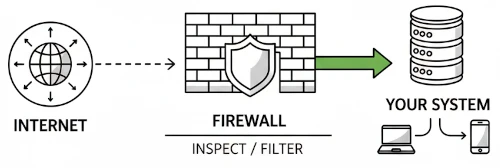
Firewalls are a core layer of defense with modern versions going beyond basic filtering and including deep packet inspection, application level rules, and built-in threat intelligence. But, attackers evolve too, finding ways around these new perimeters. With remote work, cloud, and hybrid networks firewall deployment is more complex. Misconfigurations, weak rules, and poor monitoring can expose vulnerable or unprotected services. Firewalls work by blocking attacks and stopping unauthorized access, but only when configured and managed properly.
See your Network the way Attackers Do
To understand how exposed/vulnerable your systems are to external attackers, you need to view them from the outside in. An external port scan will map what services an attacker could discover when probing your Internet-facing systems.
Mapping the Perimeter
Your network perimeter might look like:- A single IP gateway at your office
- A hosted internet server. For example: web or mail server
- An entire network range. For example, a public facing net block or ASN
System administrators, analysts, and technical operations all use external port scanning to help uncover misconfigurations and minimise their attack surface. Testing should be performed at least monthly and ideally scheduled more often, to monitor for changes to the perimeter.
Home Router Firewall
For many users, a home router provided by an ISP or purchased off the shelf is the only firewall device they will have to manage. These will perform a few roles including routing, wireless access point, network address translation (NAT) and basic packet filtering. While convenient, they also create a single point of failure in home security making it important to understand firewall and port management functions.
A recent example of an router compromise is the ASUS backdoor campaign which Greynoise discovered in May 2025. Attackers compromised thousands of ASUS routers which were exposed to the internet. Using authentication bypass including brute force login attempts to gain access. Then exploited CVE-2023-39780 which is a command injection vulnerability to run system commands. Once they got inside they used SSH on a custom port and stored a back-door.
Home users are at risk with this compromise as many homes these days have cameras, smart devices and may be forwarding ports. Once the router is compromised all the internal devices are more exposed.
What should you do? well in the instance of the above mentioned compromise read ASUS official statement for instructions. But the first thing: Run a Port Scan. Use the Online firewall test or our Online Port scanner. Check if your router is exposing SSH, admin ports, unusually high ports or any port your don't expect (in this example it was port TCP/53282).
Port Management and Firewall Administration
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding is probably the main way home users interact with firewall rules. This allows traffic form the internet to be directed to a device inside your network eg a remote desktop, a gaming server or security camera system.
Each forwarded port increases the attack surface. So if a service doesn't need to be accessible from the internet than don't forward it. A quick external port scan can show you which ports are exposed.
A practical example of port forwarding could be a home user sets up port forwarding for TCP 3389 so they can use Remote Desktop (RDP) to connect to their PC from work. Has to be done, but does expose RDP to the entire internet. This makes RDP a common target for brute-force attacks.
Firewall Administration
Firewall administration covers all the policies that control what traffic flows in and out of the network. For example, which ports and services are accessible, inbound rules (ingress filtering) and Outbound Rules (egress filtering) among others.
The primary function of firewall is to block unauthorised packets from reaching services that are listening for connections. A firewall can be situated on the network perimeter of an organisations network, inside the network, or it can directly on a host, running on the server or workstation.
Firewall administration in larger and more complex setups may involve managing multiple firewalls and filtering devices. It can include managing hundreds of rules across routers, servers and endpoints.
Example: Firewall Layers in a Small Organisation
e.g Fortinet, Palo Alto, Cisco ASA
e.g Linux iptables or Windows Firewall
e.g Windows Defender Firewall
NAT vs Firewall
Both affect how traffic moves through your router. But they serve a different purpose. NAT hides your devices, but firewall rules and port management decide what stays blocked.
NAT is about address sharing. Internal devices (eg 192.168.1.x) connect to the internet through the routers single public IP assigned by ISP. A device from the outside doesn't know the private IP Address of an internal device, it only sees the router's public IP address as the NAT drops unsolicitied inbound connection requests. So it provides a basic level of network isolation.
Firewalls and port management are what controls access. If you choose to configure Port Forwarding on a router you are bypassing this level of network isolation NAT provies and the service or device becomes directly exposed to the internet.
Port Scanning
A port scan gives you a fast, accurate view of which services are reachable without combing through and piecing together how it fits with the other networking kit. To effectively test a firewall and network perimeter the scan must be run from a remote host (ie outside your network). Our hosted online port scanner service lets you test a single IP or a whole range. All 65535 ports tested at the click of a mouse, and results delivered to your email address for review.
Example Port Scan OutputStarting Nmap 7.95 ( https://nmap.org ) at 2025-09-09 12:00 UTC Nmap scan report for 45.0.113.45 Host is up (0.032s latency). Not shown: 65532 filtered ports PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION 22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.9 (protocol 2.0) 80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.57 443/tcp closed https 3389/tcp filtered ms-wbt-server
- open: TCP Handshake Established meaning a service is available.
A connection to a listening service has been made. This state should only be found on services that have a requirement to be externally facing (HTTPS 443 80 and SMTP 25 are two examples of common external facing services). - closed: Packet is Denied - response sent.
Shows the firewall/router is passing the packet, but host isn't using that port. - Filtered: Packet is dropped by firewall or router.
Recommended state for any port that does not have a listening service on it and doesn't need to be exposed.
Note: Advanced scans may also return states such as Unfiltered or Open|Filtered when the scanner cannot clearly determine the result, but the three above are the most common in practice.
Service and Network Mapping
Port scanning isn't just about open ports. Most scanners, like Nmap, also perform service detection eg Apache on 80, OpenSSH on 22, and basic OS fingerprinting. For admins, this is a quick way to verify whats really exposed and spot changes in the network.
Troubleshooting Network Services
When installing and configuring Internet-facing services, things don't always work as expected and it will often be necessary to troubleshoot a network configuration to get a service up and running. A service may be running fine on the server but firewall rule may be blocking access from the outside.
Running an external port scan is one of the fastest ways to pinpoint the issues. If you can connect to a service from the internal host but unable to connect from external, you can make a pretty good guess the problem is likely the firewall or router. A scan from outside confirms the port is blocked helping to narrow down the focus on your troubleshooting.
Example Troubleshooting checklist:- From inside you can reach http://exampleip with no issues.
- From the internet the site doesn't load.
- An external port scan shows port 80/tcp is filtered.
This shows the web server is running, but your firewall is blocking port 80 from the outside. This kind of rule is known as ingress filtering; controlling what traffic can come in from the internet. Firewalls also enforce egress filtering, which controls what leaves your network.
Conclusion
Firewalls, NAT, and port management all work together to shape what the internet can see of your network. By running an external port scan you get the same view an attacker does. You may be troubleshooting a single host or reviewing the perimeter of an entire organisation, the process is the same: test from the outside, confirm whats open and lock down anything that doesn't need to be reachable.
Vulnerability Scans and Network Intelligence
Use CasesEnumerate and Discover
Know the Network
28 vulnerability scanners and network tools
Membership